The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test, is a common blood test that measures your average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. It's a crucial tool for diagnosing and managing diabetes, providing valuable insights into how well your blood sugar control is maintained.
Understanding the A1C Test
When you consume food, your blood sugar levels rise. Hemoglobin, a protein in your red blood cells, transports oxygen throughout your body. As blood sugar levels rise, glucose molecules attach to hemoglobin, forming glycated hemoglobin or HbA1c. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of about 120 days, the A1C test reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
A1C Test Results and Implications
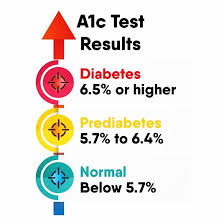
The A1C test result is reported as a percentage. A normal A1C level is below 5.7%. A level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, a condition that increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
Importance of the A1C Test
The A1C test is an essential tool for:
Diagnosing diabetes: An A1C level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests can diagnose type 2 diabetes.
Monitoring diabetes management: Regularly checking your A1C levels helps assess how well you're managing your blood sugar levels and whether your current treatment plan is effective.
Reducing the risk of diabetes complications: Lower A1C levels are associated with a lower risk of developing diabetes complications, such as heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Factors Affecting A1C Levels
Several factors can influence your A1C levels, including:
Blood sugar control: The more frequent and severe your blood sugar spikes, the higher your A1C level will be.
Age: A1C levels tend to increase with age, even in people without diabetes.
Ethnicity: African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and Asian Americans are more likely to have higher A1C levels than Caucasians.
Pregnancy: A1C levels may be lower during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
Getting an A1C Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that requires no fasting or special preparation. A blood sample is drawn from your arm, and the results are typically available within a few days.
A1C Test Results
A normal A1C level is below 5.7%. A level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, a condition that increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. The A1C test is an important tool for managing diabetes because it can help you track your blood sugar control over time. If your A1C level is high, it means that your blood sugar levels have been high for an extended period of time. This can increase your risk of developing complications of diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Discussing A1C Test Results with Your Doctor
Once you receive your A1C test results, discuss them with your doctor. They will interpret your results in the context of your overall health and medical history, providing personalized guidance on managing your blood sugar levels and reducing your risk of diabetes complications.
Remember, the A1C test is just one piece of the puzzle in managing diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to your treatment plan are equally important for maintaining good blood sugar control and preventing diabetes complications.


No comments:
Post a Comment